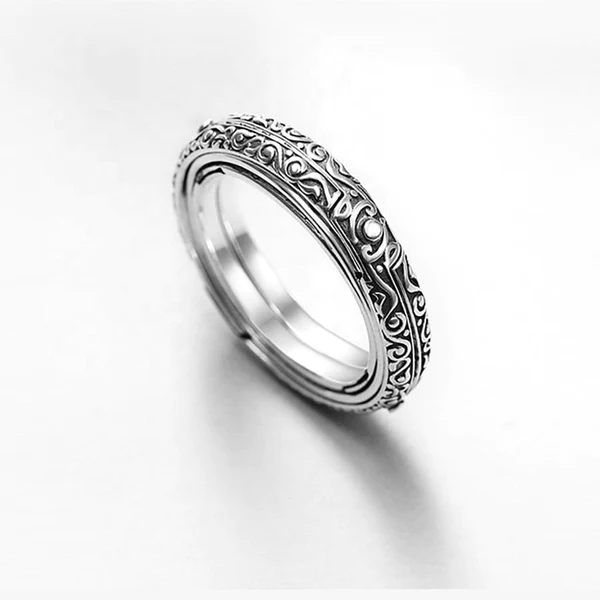
16th Century German Astronomical Ring
Original price was: $45.90.$21.80Current price is: $21.80.
CLOSE IS LOVE, OPEN IS THE WORLD
WEAR THE ENTIRE UNIVERSE ON YOUR FINGER!
Design Explanation
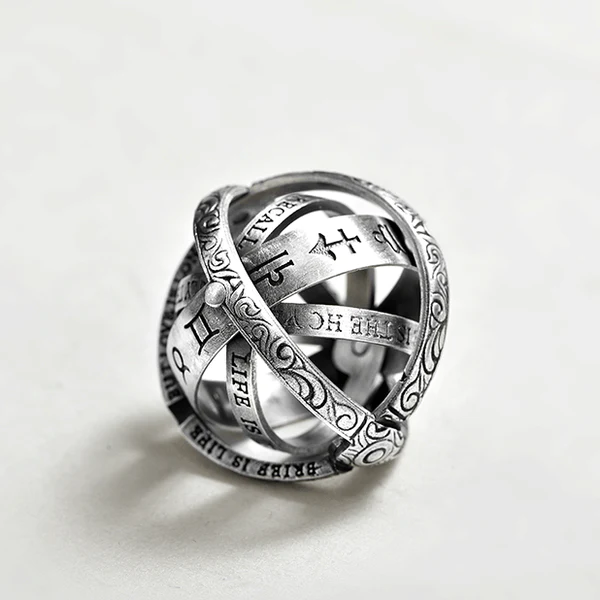
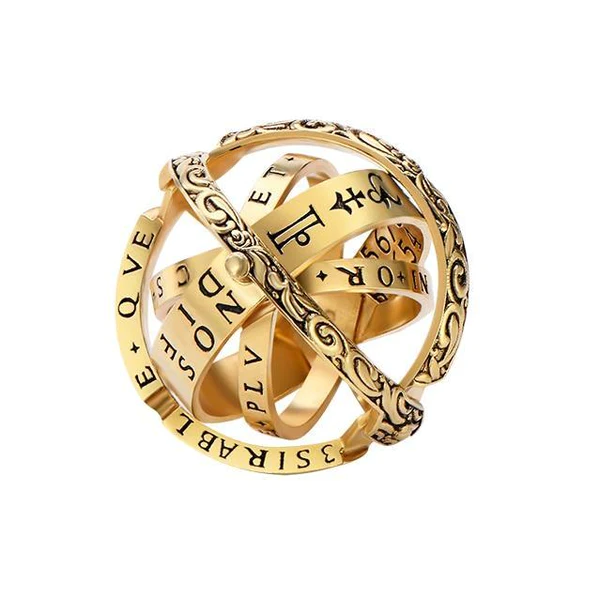
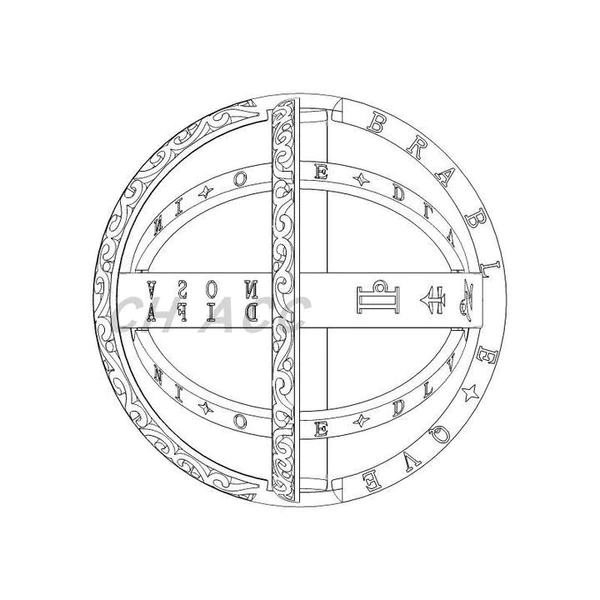
This 16th Century Astronomy Ball Ring was originally designed in the 1530s by Gemma Frisius, a famous German astrologer, philosopher, and instrument maker. Back then, the ring was used as an instrument to tell time and help with navigation.
And today, with the help of skilled modern craftsmen, the mysterious cosmic ring is now turned into an elegant vintage astronomy ball. Not only does it contain the star signs of the universe, but it also represents life and love.

Romance 500 years ago, “Closing is love, opening is the world”.
Feature
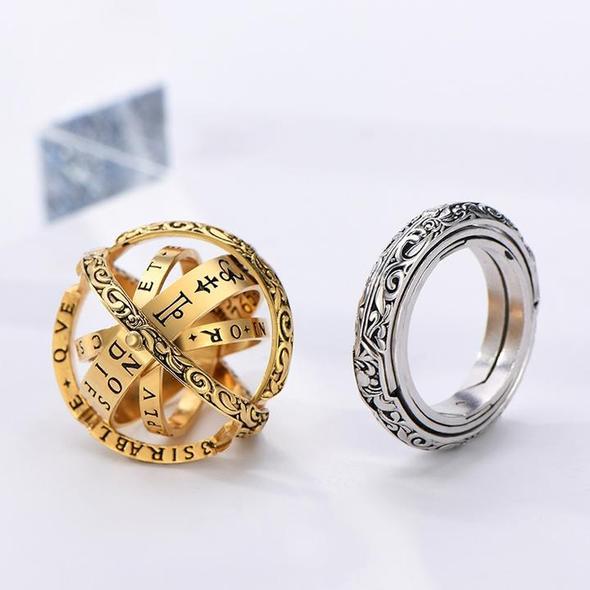
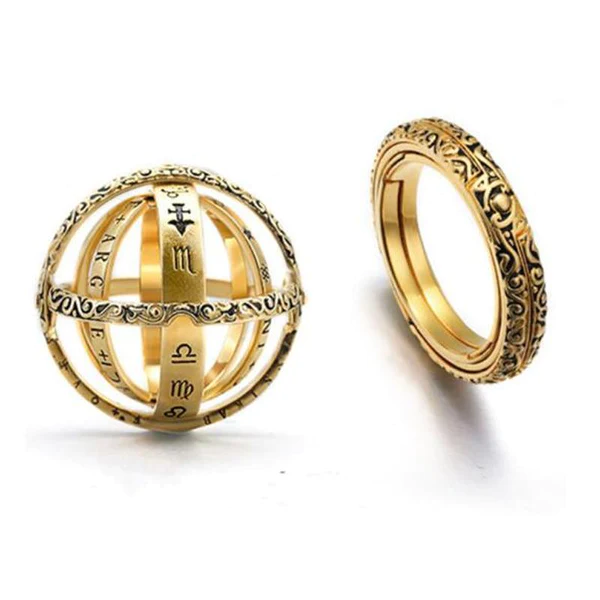
- 【Sophisticated Body Ring】The combination is a delicate ring, unfolding is an astronomical ball, the temptation of the fingertips hiding the entire universe.As the different bands are fanned out, the rings take on a unique quality.
- 【Unique Design】 It is engraved with astronomical symbols from the 16th century, Zodiac, Ancient Greek alphanumeric characters, constellations, etc. Waiting for your discovery.
- 【Rustproof Material】It’s skillfully crafted and carefully inscribed to satisfy your cosmic curiosity.
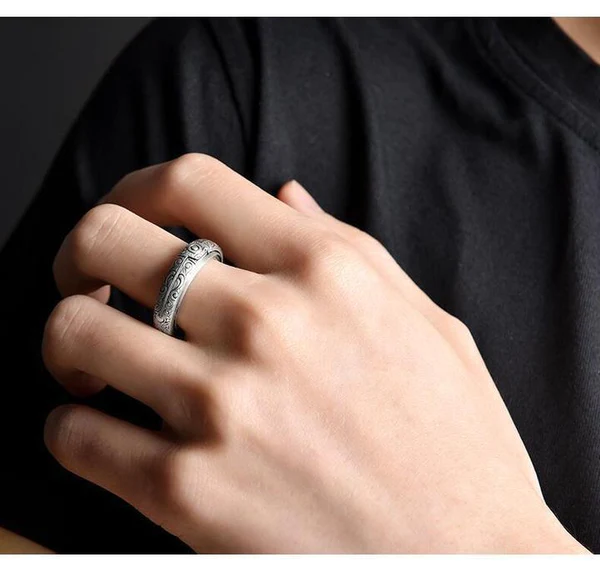
- 【Wear it in 2 ways】Wear it as a ring…or as a pendant hanging by your favorite plain necklace. Either way, it adds a classically elegant touch to any daily attire!
- 【Romantic For Her/Him】The most romantic thing that I can think of is just to give the whole world to you. It’s the perfect gift for yourself, your friends or families, and all the other astronomy lovers out there.

If not, measure your finger:
- Wrap a strip of paper around your finger, just above the knuckle, and mark the point at which the two ends meet.
- Measure the paper from mark to mark to find your ring circumference (mm).
- Check Below Ring Size to locate your size.
An astronomical ring is an ancient method used to determine the position of the sun. These rings are typically made out of wood, rock or glass, and are often painted black or white. They are very accurate, although the accuracy depends on the skills of the person making them, and the conditions under which they are measured.
History of Astronomical Rings
The ancient Greeks invented many things that are used today, including the compass and the telescope. They also developed the concept of zero, which is now widely used in mathematics. Their invention of the astrolabe allowed astronomers to measure the position of celestial objects such as stars and planets. This led to advances in astronomy, navigation, cartography and surveying.
In 1674, Sir Isaac Newton published his theory of universal gravitation, which stated that every object attracts every other object around it with a force directly proportional to the product of those objects’ masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. His work laid the foundation for classical mechanics and modern physics.
Newton’s law of cooling states that heat flows spontaneously from hotter bodies to colder ones. He also discovered the laws of motion and optics.
Types of Astronomical Rings
There are several ways to classify astronomical objects based on how close they orbit around another object. These orbits are called planetary systems. If you think about it, there are really only two kinds of planetary systems: those where one planet orbits the star, and those where multiple planets orbit the same star. This distinction becomes important because each system has a unique set of characteristics that affect how the system evolves over time.
In our solar system, the Sun is the center of everything. All the planets revolve around the Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. Our solar system is known as a single-planet system because the Sun is the only planet orbiting the central star. Single-planet systems are very common among stars similar to our Sun. Some stars have no planets at all, while others host multiple planets.
Planetary systems can be classified into four major groups:
1. Circular Orbits – One planet orbits the star.
2. Eccentric Orbits – Two planets orbit the star.
3. Resonant Orbits – Three or more planets orbit the star. Each planet is located in a resonance zone, meaning that the distance between the planets is equal to some integer fraction of the orbital period of the outermost planet.
Sun Ring
A sun ring is an instrument that measures the position of the Sun in the sky. They are often referred to as “sun rings”, though that term usually refers to a different device.
The sun ring consists of a horizontal arm attached to a vertical rod. At one end of the arm is a small disc, while at the other is a larger disc. The smaller disc casts a shadow onto the ground, while the larger disc does not. As the Sun moves across the sky, it casts a shadow onto the surface of the earth. When the Sun reaches the edge of the smaller disc, the shadow falls onto the ground. This indicates that the Sun is directly overhead. If the shadow falls onto the larger disc, the Sun is lower in the sky. In this case, the Sun is either setting or rising.
In addition to indicating whether the Sun is high or low, the sunring can tell you how far away the Sun is. For example, if the shadow is halfway between the two discs, the Sun is about half way up the sky.
Traveller’s Sundial or Universal Equinoctal Ring Dial
A traveller’s sundial uses shadows cast by sunlight to determine time of day. These devices were used by travellers since antiquity. In the Middle Ages, travellers carried small pocket versions called “traveler’s rings”. Travelers could use the device to find out what time it was at home, even if they had no access to a clock.
The earliest known traveler’s sundials date back to Roman times. They were used by soldiers during the Roman Empire. Soldiers needed to know the local time while travelling, because they needed to make sure that they arrived at their destination before nightfall.
In medieval times, travelers carried small pocket versions called traveler’s rings. They were usually made of wood, metal or ivory. The oldest surviving example dates back to the 13th century.
Today, most modern traveler’s sundials are digital. Some models include a solar panel, battery and display screen; others just require a power source such as USB. Many models have adjustable settings.
Sea Ring
The sea ring is one of the oldest methods of determining the time. There are several different types of sea rings, including the sun dial, moon dial, and water clock. These instruments use the position of the Sun or Moon to indicate the time.
A sundial is an instrument used for measuring the passage of Time. They are usually outdoor devices, although some indoor versions exist. Sundials are very useful because they allow you to see the time without needing to look at a watch, clock, or phone.
Structure and Function
Solar elevation refers to the angle between the sun and the horizon. This angle changes throughout the day and during the seasons. In winter, the sun rises high in the sky while it sets low in the summer.
The average solar elevation varies depending on location. For example, in New York City, the sun rises around 9 AM and sets around 5 PM. However, in Phoenix, Arizona, the sun rises around 7 AM and sets around 3 PM.
There are many different instruments available for measuring solar elevation. Some people prefer to use a compass and a protractor. Others use a laser range finder or a GPS device.
Astronomical Rings
The Renaissance Period was a time of great change in Western Civilization. During this time, many different types of art forms flourished, including jewelry. Jewelry became much more elaborate, and many different styles emerged. One style that developed during this time was the ring. Rings were originally used to signify ownership, but soon became symbols of love and affection. In fact, some of the earliest rings were made out of precious metals like gold and silver. However, in later centuries, rings became less important, and were replaced by necklaces. Today, we still use rings as symbols of friendship and romance.
17th Century Foldable Ring Based on Ancient Astronomical Tool
These rings were worn by scientists throughout the 17th century. They were based on an ancient astronomical tool called an armillary sphere—a device used to measure celestial bodies like stars and planets. A modern version of this ring is now being offered online.
The rings were made with multiple rings which moved together to form an armillar sphere. Each ring had one side engraved with symbols representing the signs of the zodiac. On each finger there were four rings; two small ones on the thumb and forefinger, and two larger ones on the middle and little fingers. The rings could be folded up into a compact shape, making it easy to carry around.
This type of ring is still very much in use today. In fact, many people wear one just because they look cool. There are even some companies selling jewelry inspired by the design.
The rings are called armillary circles because they resemble the shapes of armillary spheres, which are devices used to measure astronomical phenomena. Armillary spheres date back to the 3rd century BC, but it wasn’t until 1603 that Galileo Galilei developed his version of the device. His design was based on the work of Ptolemy, an ancient Greek astronomer who lived around 150 AD.
Galileo’s invention consisted of three concentric rings attached to each other with hinges. Each ring had different sizes and diameters, allowing the user to determine the position of the sun, moon, planets, stars, etc., depending on how far apart the rings were placed.
Today, armillary circles are still used to track the positions of celestial objects. However, they aren’t always practical for everyday use. For instance, you’d probably want something smaller than a full-size armillary circle if you’re planning on tracking the movements of the moon during a lunar eclipse.
The Astronomical Ring – An Ancient Astronomy Tool
In the late 1800s, the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander invented what he called “the great astronomical ring,” a device that allowed him to calculate the positions of the planets in the night sky. This invention became known as the Argand telescope because it looked like a giant hourglass. The ring consisted of three parts: a central disc, a pair of arms extending outwards from each side of the center, and a small handle attached to one end of the arms. When the handle was turned, the arms moved outward or inward, allowing the observer to adjust the size of the opening in the middle of the ring.
Argand telescopes were originally used to measure the distance of heavenly objects, such as the moon or sun. In addition, they were often used to determine the relative sizes of the planets. By measuring the angle of light reflected off of Jupiter, scientists could estimate the planet’s diameter.
These instruments were extremely expensive and required skilled operators. As a result, most astronomers didn’t use them very often. Instead, they relied on simpler devices, such as sextants, which measured angles of reflection. However, these instruments couldn’t provide accurate measurements of planetary distances.
By the early 1900s, the Argand telescope had fallen out of favor among astronomers. But today, many people wear rings similar to the ones Argand used to make his calculations. These rings are called “sun wheels.” They’re usually made of metal, wood, or plastic and feature a circular hole in the center.
One popular type of sun wheel is the “sun dial.” Sun dials work just like Argand’s original instrument. They allow you to see the exact time of day based on where the sun is located in the sky. You simply turn the dial to align the shadow cast by the sun with the markings on the face of the dial. Sun wheels aren’t limited to just showing the time of day. Some models include a compass inside of the circle, while others have a scale that allows you to measure the length of shadows.
Gifts For Designers | 16th Century German Astronomical Ring | A Token of Love
This 16th Century Astronomy Ball Ring was originally designed in the 1530s by Gemma Frisius, a famous German astrologer, philosopher, and instrument maker. Back then, the folding ring was used as an instrument to tell time and help with navigation.
And today, with the help of skilled craftsmen, the mysterious cosmic ring is now turned into an elegant vintage astronomy ball. Not only does it contain the star signs of the universe, but it also represents life and love.
Featuring:
- Sophisticated Body Ring: The combination is a delicate zodiac ring, unfolding is an astronomical ball, the temptation of the fingertips hiding the entire universe. As the different bands are fanned out, the rings decorative elements take on a unique quality.
- Unique Design: It is engraved with astronomical symbols from the 16th century, Zodiac, Ancient Greek alphanumeric characters, constellations, etc. Waiting for your discovery.
- Rustproof Material: Its metal rich material has been skillfully crafted and carefully inscribed to satisfy your cosmic curiosity.
- Wear it in 2 ways: Wear it as a ring…or as a pendant hanging by your favorite plain necklace. Either way, it adds a classically elegant touch to any daily attire!
- Romantic For Her/Him (Unisex Ring): The most romantic thing that I can think of is just to give the whole world to you. It’s the perfect gift for yourself, your friends or families, and all the other astronomy lovers out there.
Specifications
- Material: Alloy/ Sterling Silver Plated
- Color: Gold/ Silver
- Size: 5-10 (49.3 – 62 mm)
- Thickness: About 0.25cm
- Wight: About 10g

Package Included:
- 1 x 16th Century German Astronomical Ring
- 1 x necklace (if ordered)
Ring Size Instruction
If you have an existing ring:
- Measure the diameter (mm) of a ring that fits the desired finger.
- Check Below Ring Size to locate your size.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.